Sequential Quantum Gate Decomposer (SQUANDER) v1.8.8 is an open source software distributed under the GNU General Public License. The project was supported by OTKA PD123927 grant and by the Ministry of Innovation and Technology and the National Research, Development and Innovation Office within the Quantum Information National Laboratory of Hungary.
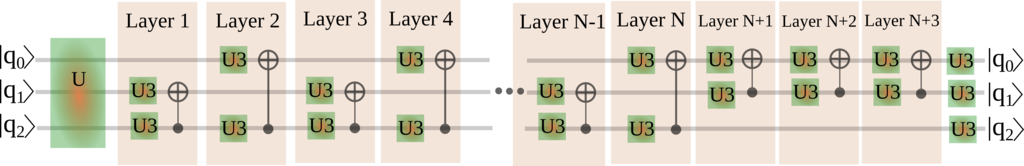
The SQUANDER package provides a novel solution to decompose any n-qubit unitaries into a sequence of one-qubit rotations and two-qubit controlled gates (such as controlled NOT or controlled phase gate). SQUANDER utilizes two novel gate synthesis techniques reported in Refereces [1] and [2]. (i) To synthesize general unitaries SQUANDER applies periodic layers of two-qubit and parametric one-qubit gates to an n-qubit unitary such that the resulting unitary is 1-qubit decoupled, i.e., is a tensor product of an (n-1)-qubit and a 1-qubit unitary. Continuing the decoupling procedure sequentially one arrives at the end to a full decomposition of the original unitary into 1- and 2-qubit gates. SQUANDER provides lower CNOT counts for generic n-qubit unitaries (up to n=6) than the previously provided lower bounds. (ii) An adaptive circuit compression is used to optimize quantum circuit by the application of parametric two-qubit gates in the synthesis process. The utilization of these parametric two-qubit gates in the circuit design allows one to transform the discrete combinatorial problem of circuit synthesis into an optimization problem over continuous variables. The circuit is then compressed by a sequential removal of two-qubit gates from the design, while the remaining building blocks are continuously adapted to the reduced gate structure by iterated learning cycles.
[1] Péter Rakyta, Zoltán Zimborás, Approaching the theoretical limit in quantum gate decomposition, arXiv:2109.06770.
[2] Péter Rakyta, Zoltán Zimborás, Efficient quantum gate decomposition via adaptive circuit compression, arXiv:2203.04426.
The SQUANDER library is written in C/C++ providing a Python interface via C++ extensions. The present package is supplied with Python building script and CMake tools to ease its deployment. The SQUANDER package can be built with both Intel and GNU compilers, and can be link against various CBLAS libraries installed on the system. (So far the CLBAS libraries of the GNU Scientific Library, OpenBLAS and the Intel MKL packages were tested.) In the following we briefly summarize the steps to build, install and use the SQUANDER package.
Contact Us
Have a question about the SQUANDER package? Don't hesitate to contact us at the following e-mails:
Zoltán Zimborás (researcher): zimboras.zoltan@wigner.hu
Peter Rakyta (developer): peter.rakyta@ttk.elte.hu
Dependencies
The optimization algorithm of SQUANDER relies on the multimin component of the GNU Scientific Library. We developed and tested the SQUANDER package with GNU Scientific Library of version 2.5 and 2.6. The dependencies necessary to compile and build the SQUANDER package are the followings:
- CMake (>=3.10.2)
- GNU Scientific Library (>=2.5, shipped with the gsl python package)
- C++/C Intel (>=14.0.1) or GNU (>=v4.8.1) compiler
- TBB library
- Intel MKL (optional)
- OpenBlas (optional, recommended)
- Doxygen (optional)
The Python interface of SQUANDER was developed and tested with Python 3.6-3.9. The SQUANDER Python interface needs the following packages to be installed on the system:
How to build GNU Scientific Library
In order to build and use the SQUANDER we recommend the Anaconda virtual python environment providing all the required dependencies for SQUANDER. One can easily install the GNU Scientific Library for local users by the command
Here we describe an alternative way to deploy GNU Scientific Library from source by the end user without administrative privileges. The GNU Scientific Library can be downloaded from the site https://www.gnu.org/software/gsl/. After the downloaded package is extracted somewhere in the home directory of the user (path/to/gsl/source), one should configure the compiling environment using the configure tool. Depending on the individual settings the default compiler to be invoked might be different from HPC to HPC. To ensure the usage of the GNU compiler, the following shell command should be executed inside the directory path/to/gsl/source:
(Similarly, Intel compiler can be forced by setting FC=ifort CC=icc and CXX=icpc.) The installation directory of the compiled GNU Scientific Library is given by –prefix=path/to/gsl (which is different from the directory path of the source files given by path/to/gslsource). To install GNU Scientific Library the user should have read and write permissions on the path path/to/gsl (which might be for example /home/username/gsl). After the successful configuration the GNU Scientific Library can be compiled by the shell command
The compilation of the GNU Scientific Library takes some time. When the compilation is done, the package (including the C header files and the static and shared libraries) is installed into the directory path/to/gsl by the shell command:
Download the SQUANDER package
The developer version of the SQUANDER package can be downloaded from github repository https://github.com/rakytap/quantum-gate-decomposer/tree/master. After the package is downloaded into the directory path/to/QGD/package (which would be the path to the source code of the SQUANDER package), one can proceed to the compilation steps described in the next section.
How to build the SQUANDER package
The SQUANDER package is equipped with a Python build script and CMake tools to ease the compilation and the deployment of the package. To ensure that SQUANDER package would find the necessary libraries and header files during compilation time it is advised to define the following environment variables:
The SQUANDER package is parallelized via Threading Building Block (TBB) libraries. If TBB is not present in the system, it can be easily installed via python package tbb-devel. Alternatively the TBB libraries can be installed via apt or yum utility (sudo apt install libtbb-dev) or it can be downloaded from https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneTBB and built from source. In this case one should supply the necessary environment variables pointing to the header and library files of the TBB package. For newer Intel compilers the TBB package is part of the Intel compiler package, similarly to the MKL package. If the TBB library is located at non-standrad path or the SQUANDER package is compiled with GNU compiler, then setting the following environment variables:
When the TBB library is installed via a python package, setting the environment variables above is not necessary. The SQUANDER package with C++ Python extensions can be compiled via the Python script setup.py located in the root directory of the SQUANDER package. The script automatically finds out the CBLAS library working behind the numpy package and uses it in further linking. The setup.py script also build the C++ library of the SQUANDER package by making the appropriate CMake calls.
Developer build
We recommend to install the SQUANDER package in the Anaconda environment. In order to install the necessary requirements, follow the steps below:
Creating new python environment:
Activate the new anaconda environment
Install dependencies:
After the basic environment variables are set and the dependencies are installed, the compilation of the package can be started by the Python command:
The command above starts the compilation of the SQUANDER C++ library and builds the necessary C++ Python interface extensions of the SQUANDER package in place. After a successful build, one can register the SQUANDER package in the Python distribution in developer (i.e. editable) mode by command:
Binary distribution
After the environment variables are set it is possible to build wheel binaries of the $QGD package. In order to launch the compilation process from python, scikit-build package is necessary. (It is optional to install the ninja package which speeds up the building process by parallel compilation.) The binary wheel can be constructed by command
$ python3 setup.py bdist_wheel
in the root directory of the $QGD package. The created $QGD wheel can be installed on the local machine by issuing the command from the directory path/to/SQUANDER/package/dist
We notice, that the created wheel is not portable, since it contains hard coded link to external libraries (TBB and CBLAS).
Source distribution
A portable source distribution of the SQUANDER package can be created by a command launched from the root directory of the SQUANDER package:
In order to create a source distribution it is not necessary to set the environment variables, since this script only collects the necessary files and pack them into a tar ball located in the directory path/to/SQUANDER/package/dist. In order to install the $QGD package from source tar ball, see the previous section discussing the initialization of the environment variables. The package can be compiled and installed by the command
issued from directory path/to/SQUANDER/package/dist (It is optional to install the ninja package which speeds up the building process by parallel compilation.)
How to use
The algorithm implemented in the $QGD package intends to transform the given unitary into an identity matrix via a sequence of two-qubit and one-qubit gate operations applied on the unitary. Thus, in order to get the decomposition of a unitary, one should rather provide the complex transpose of this unitary as the input for the $QGD decomposing process, as can be seen in the examples.
Python Interface
The SQUANDER package contains a Python interface allowing the access of the functionalities of the SQUANDER package from Python. The usage of the SQUANDER Python interface is demonstrated in the example files in the directory examples located in the root directory path/to/QGD/package, or in test files located in sub-directories of path/to/QGD/package/qgd_python. The example files can be run similarly to any python scripts, while the test files can be invoked by the pytest utility. The example files import the necessary qgd_python modules containing the wrapper classes to interface with the C++ SQUANDER library. (So the $QGD package need to be installed or the compiled package needs to be added to the Python search path.)
 1.8.13
1.8.13